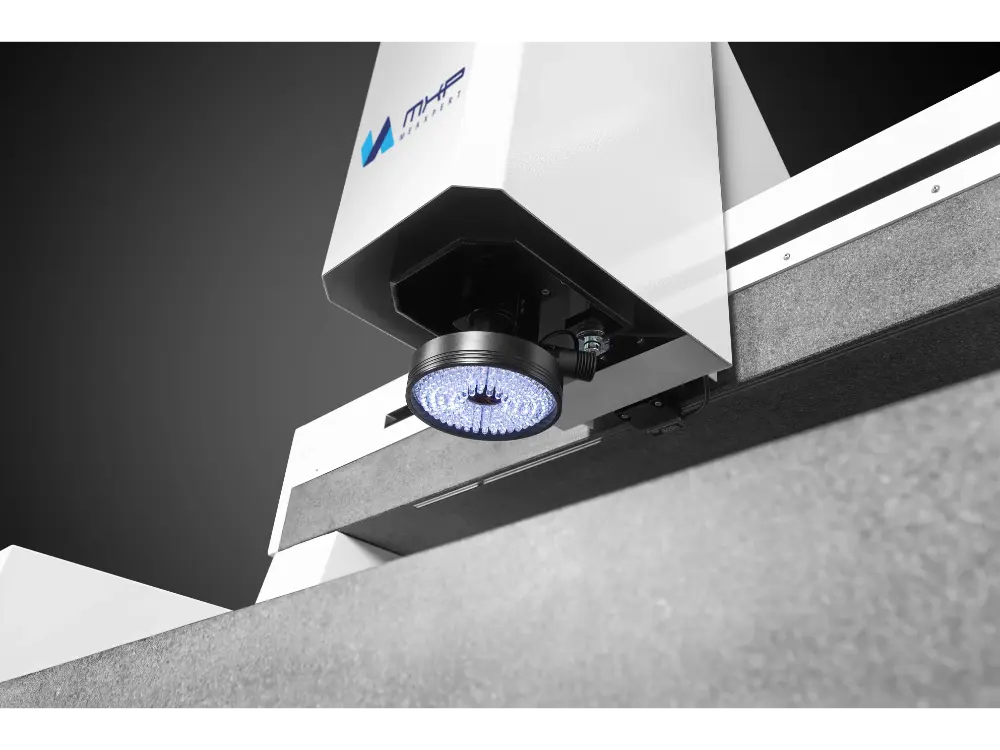

Precision measurement is a necessity for modern manufacturing production. Even the slightest deviation can lead to poor quality or high costs. Traditional tools such as calipers and gauges are reliable, but they cannot meet the demanding speed and accuracy requirements of modern complex assembly lines.
Advanced tools like coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) and vision measuring machines (VMMs) have changed 3D measurement. They meet the high-precision demands of complex shapes, angles, and distances with ease. Both are powerful, but they are applicable to different scenarios and have unique advantages. This article will take a deep look at the differences between CMMs and VMMs, their respective advantages, and how to choose the best solution for your manufacturing needs.
Was ist ein VMM?
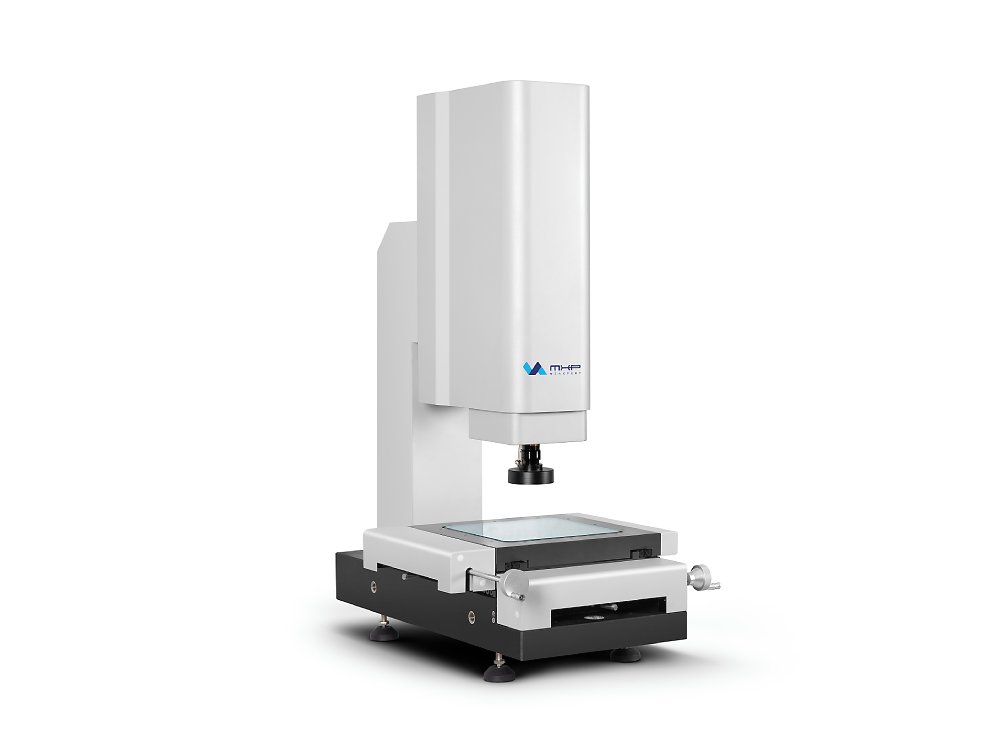

Vision Measuring machines (VMMs) are also called video-measuring systems or image-measuring systems. They are optical measuring instruments, ideal for measuring small or delicate parts. VMM machines use a non-contact measurement method, thus avoiding the risk of damage caused by physical contact.
The visual sensor is the core component of the VMM machine, which includes a camera and an optical lens. There are also laser probes and contact probes. The laser probe is used to measure transparent and translucent objects. The contact probe can measure 3D distance.
VMMs capture an object’s image with a camera and use computer software to generate a 3D model. The operator analyzes and measures linear attributes such as points, lines and angles as well as geometric attributes based on the model.
Was ist ein KMG?
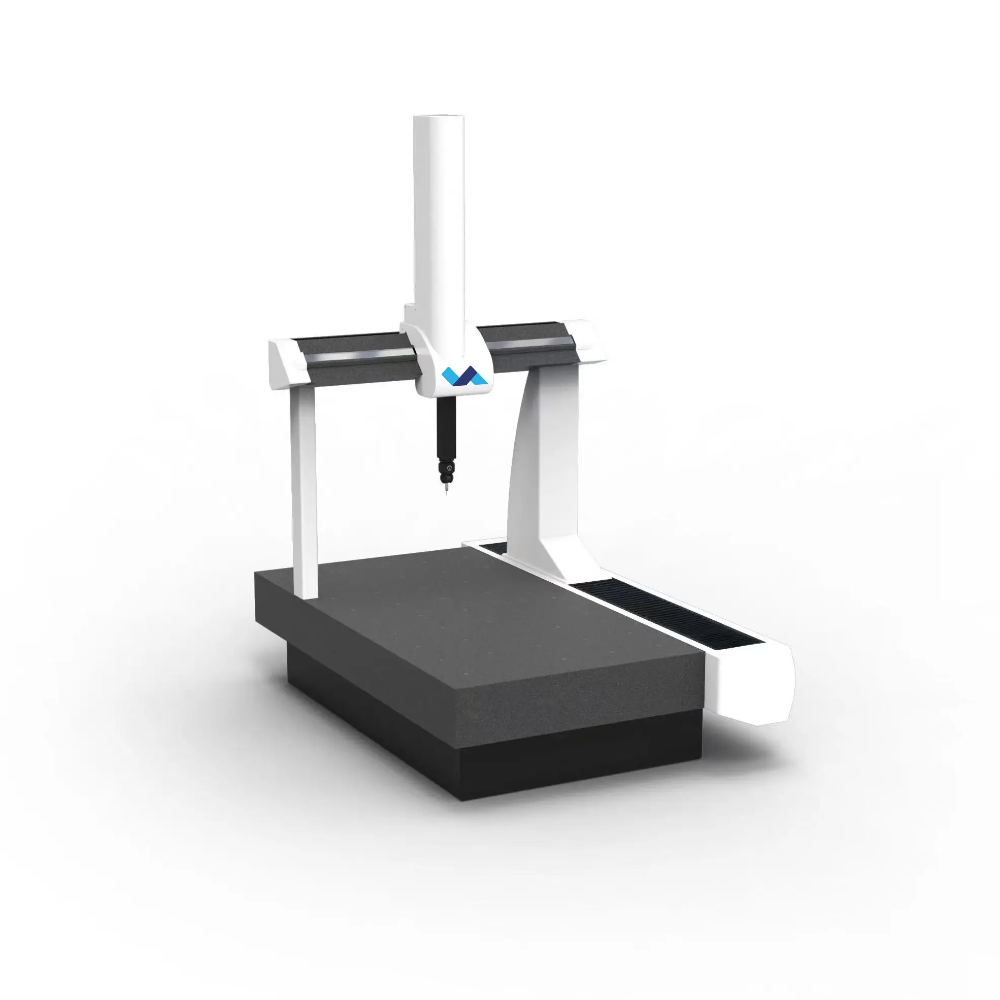
CMM stands for coordinate measuring machine, which uses a probe and computer software to analyze and measure objects. Unlike VMMs, CMMs are usually larger and have a solid granite platform, making them suitable for measuring heavy or large parts.
Coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) collect precise coordinate data by contacting different points on an object. The software then turns these coordinates into a detailed 3D CAD model. This lets users measure features like distance, angle, roundness, and geometric tolerance (GD&T). Some portable coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) now do not require a fixed workbench, making them more flexible to operate.
The Differences Between VMM and CMM
Sowohl VMM als auch CMM quantifizieren die geometrischen Merkmale eines Objekts. Sie weisen jedoch einige wesentliche Unterschiede auf. Im Folgenden werden einige wichtige Aspekte erläutert, durch die sich Bildverarbeitungssysteme und koordinatenbasierte Messmaschinen unterscheiden.
Messmethoden
VMMs use non-contact optical systems. They rely on high-resolution cameras and laser probes. These tools capture images and measure small or delicate parts without touching them. CMMs use contact probes to gather coordinate data by touching the object. They also have larger stages than VMMs. This makes CMMs better for heavy or rugged parts.
Präzision und Genauigkeit
Because VMMs use optical lenses and computer software tools, they are generally faster and easier to operate for simple measurements. VMMs offer features such as automatic edge detection, tracking, autofocus, and light adjustment tools. They can measure distances with an accuracy of up to 0.25 microns.
CMMs, while highly accurate (measuring distances with an accuracy of 2 to 5 microns), require more setup time and skilled staff to operate.
Anwendungen
VMMs are ideal for industries that require non-contact measurement of complex or fragile parts, such as electronics, machinery, and medical devices. CMMs have bigger stage areas. They are popular in aerospace, automotive, and heavy manufacturing. This includes automotive prototypes, CNC fixtures like spindles and slides, and heavy machine parts.
Kosten und Wartung
VMMs sind im Allgemeinen erschwinglich. Sie sind leichter zu warten, da sie aus weniger Bauteilen bestehen. Sie erfordern eine geringe Anfangsinvestition. Ihr Preis wird jedoch von Faktoren wie dem Bewegungsmodus der VMM, dem Sensortyp, der Softwarefunktionalität und der Hardwarekonfiguration beeinflusst.
CMMs require a higher initial investment than VMMs. They are also bulkier and have complex moving parts. For this reason, maintaining them can prove challenging. CMMs require a trained operator to work them. Factors such as professional training, work hours, and shift timings may influence the cost of operating a CMM. Other cost factors may include licensing fees, calibration costs, and replacement of probe tips.
Should I choose VMM or CMM?
Möchten Sie wissen, welche die richtige für Sie ist? Stellen Sie sich zunächst diese Fragen:
- Denken Sie an den Platz. Ist Ihre Werkstatt groß oder klein? KMGs sind groß und eignen sich möglicherweise nicht für kleine Werkstätten. VMMs hingegen sind kompakte Maschinen. Wenn Sie in einem kleinen Raum arbeiten, sind sie die ideale Wahl.
- Wie viele Teile müssen Sie an einem Tag bearbeiten? Viele Werkstätten bearbeiten täglich große Mengen von Teilen. In diesem Fall kann ein VMM ideal für Sie sein. Wenn Sie jedoch mit weniger Teilen arbeiten, sind KMGs gut geeignet. KMGs sind auch besser in der Lage, Objekte unterschiedlicher Größe zu analysieren.
- Die Art des Werkstücks, das Sie messen wollen, bestimmt auch die benötigte Maschine. Wenn Sie 3D-Objekte messen, kann ein Bildmesssystem die erforderlichen Operationen nicht durchführen. Denn die Stärke eines VMM liegt in seiner hohen Auflösung, mit der es genaue 2D-Bilder erzeugen kann.
- Wollen Sie extreme Präzision bis auf den Mikrometer genau? In diesem Fall sind VMMs vielleicht besser für Sie geeignet. Obwohl beide Maschinen hervorragend sind, bieten VMMs eine Präzision von bis zu 0,25 Mikron.
- Sind die Teile, die Sie messen, zerbrechlich oder verformbar? In diesem Fall sollten Sie sich für die VMM entscheiden. Sie sind berührungslose Maschinen. Sie können formbare Objekte messen, während KMGs dies nicht können.
Schlussfolgerung
Ob Sie sich nun für VMMs oder KMGs entscheiden, beides sind leistungsstarke Messinstrumente. Sie beschleunigen garantiert Ihren Fertigungsprozess. Mit der Wahl des richtigen Geräts optimieren Sie Ihre Mess- und Konstruktionsabläufe. Obwohl beide ähnliche Funktionen haben, sind ihre Einsatzmöglichkeiten sehr unterschiedlich. Für ein schnelleres Arbeitstempo, höhere Präzision und kleine Objekte sollten Sie sich für VMM entscheiden. Für Vielseitigkeit, 3D-Mapping und schwere Teile sollten Sie sich für das KMG entscheiden. Wenn Sie die wichtigsten Punkte aus diesem Artikel beherzigen, wird der Kauf einer Messmaschine problemlos und einfach sein.
Über MXP
MXP is a leader in VMMs and CMMs. We provide efficient, reliable, quality inspection solutions using advanced optical tech and precise measurement systems. Kontaktieren Sie uns jetzt.
